Our Blogs
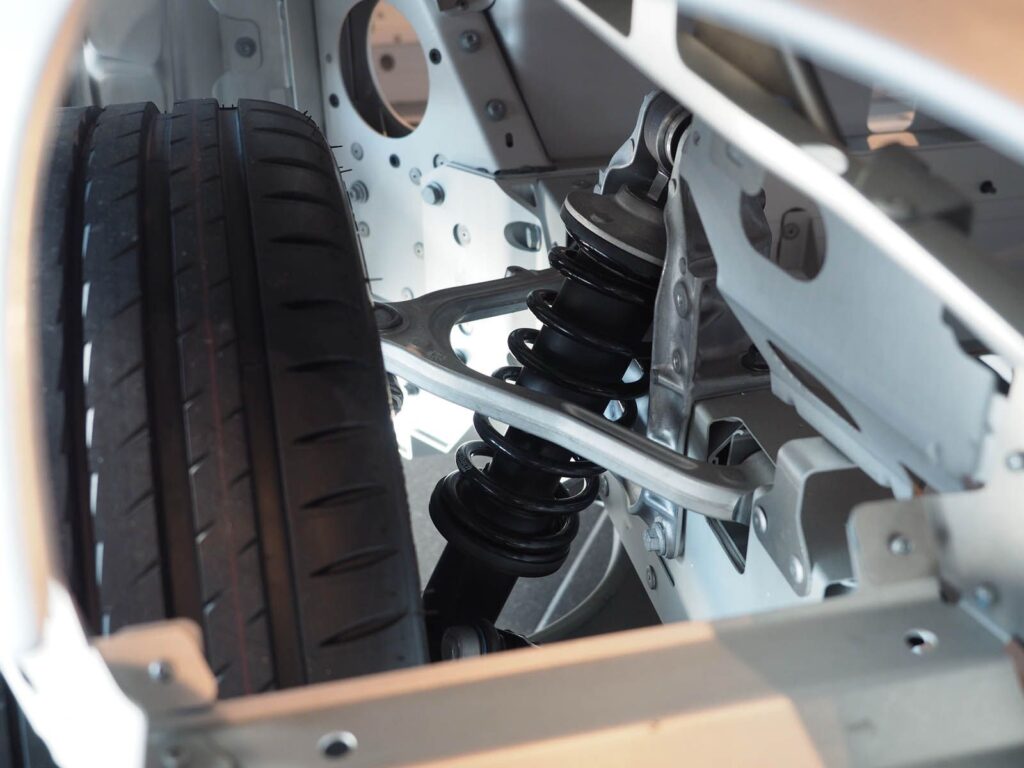

The Evolution of Automotive Materials: New Trends and Innovations
The automotive sector has experienced major advancements throughout the previous century because materials engineering improved vehicle capabilities together with safety protocols while implementing sustainable practices. The advancement of automotive materials through steel bodies into contemporary lightweight composites occurred because of their effectiveness in enhancing fuel efficiency as well as durability and safety together with sustainability concerns.
The current automotive industry puts its focus on creating cars through the combined use of environmentally friendly solutions and lightweight materials and innovative composites to improve efficiency. The blog provides a detailed overview of automotive materials starting from historical developments leading to contemporary progress and future innovations which determine the evolution of future mobility systems.
The Evolution of Automotive Materials: A Historical Perspective
- Early Automotive Materials (1900s – 1950s)
The early Car manufacturers used wood as well as iron materials to build their early vehicles which appeared similar to horse-drawn carriages. Vehicle series production made steel dominate other materials because it offered excellent strength combined with durable performance at budget-friendly costs.
The Ford Model T introduced in 1908 together with other early twentieth-century cars implemented steel construction due to their better resistance in their frames and body structure.
Safety glass became available in the 1920s because it served as a windshield solution which protected drivers from windshield shattering injuries.
Improved road grip attributes from pneumatic rubber tires brought better comfort to automotive vehicles as a result of their growth in popularity.
The automotive industry began using aluminum and magnesium materials in World War II military vehicles because of lightweight characteristics to establish fundamental principles for future production methods.
- The Rise of Aluminum and Plastics (1960s – 1980s)
Vehicle manufacturers picked lightweight materials due to higher petroleum prices throughout the 1960s through 1970s period.
Aluminum materials became a manufacturing priority for engine blocks and transmission cases as well as body panels in the Chevrolet Corvette’s fiberglass body structure.
The production of vehicles became more cost-effective through the use of plastic materials which are also called polymers and plastics. Computer-driven technology enabled a substantial growth of plastic use throughout vehicle dashboards as well as interior trims and bumpers.
Safety Improvements: The development of crumple zones and impact-absorbing materials in the 1970s enhanced passenger safety
- The Age of Advanced Composites & High-Strength Steel (1990s – 2010s)
During the late 20th century car manufacturers prioritized obtaining elemental materials that simultaneously reduced weight while delivering better performance and reliability and durability.
Modern steel alloys referred to as High-Strength Steel delivered outstanding crash safety without compromising weight reduction performance.
All three premium car companies BMW, Ferrari and McLaren used carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP) to build their high-performance lightweight models.
The introduction of hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) compelled car manufacturers to adopt lightweight aluminum with composite materials for balancing EV battery weight.
New Trends in Automotive Materials (2020s & Beyond)
- Lightweight Materials for Fuel Efficiency & EVs
The challenge to create vehicles with higher efficiency and extended battery capacity makes manufacturers use these lightweight materials:
The aluminum alloy materials appear across multiple Tesla products and Ford and Jaguar vehicles to create possible weight decreases.
The shifting industry trend from aluminum to magnesium alloys occurred because magnesium provides better weight reduction for applications that require weight optimization.
The high costs of CFRP materials restrict their market entry into luxury performance vehicles despite their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
- High-Strength & Advanced Steel
The automotive industry depends on steel throughout its core components despite framework specialists choosing UHSS and AHSS steels due to their superior crash-resistance capability which leads to weight conservation of between 30-40% compared to traditional steel components.
The entirety of vehicles feature AHSS in their frames since it ensures enhanced protection in case of accidents.
Manufacturers in the steel sector integrate various lightweight elements into steel products to develop advanced items which merge reduced weight with superior performance capabilities.
- Sustainable & Eco-Friendly Materials
The automotive industry tracks down environmentally-friendly materials that can break down and permit the wheel of material reuse.
Automobile manufacturers transform corn together with soybean and sugarcane materials into plastic products to help lower their petroleum-based material use.
Businesses dedicate their efforts to establish methods that recycle carbon fiber waste produced by airplane and automotive industries.
The alliance of hemp fiber with flax and kenaf functions as sustainable fiber composites used today within automotive products including dashboards and door trims because of weight reduction and sustainable advantages.
- Smart & Adaptive Materials
New generation vehicles incorporate smart materials able to change their behavior based on different driving environments together with suitable operating conditions.
The utilization of Shape-Memory Alloys (SMA) enables materials to change form when temperatures change thus resulting in better efficiency combined with better aerodynamic performance.
The polymers’ ability to heal themselves permits them to repair small scratches and dents on vehicle surfaces automatically.
A combination of nanotechnology allows producers to make protective coatings that prevent scratches and handle self-cleaning functions while blocking UV rays.
- 3D Printing & Custom Materials
The automotive sector receives advantages from 3D printing technologies because they revamp product components while optimizing materials use.
3D printing methods enable manufacturers to carry out quick new material and component tests for rapid prototyping operations.
Automation producers alongside aftermarket companies carry out personalized light-weight part production and component repairs using on-demand manufacturing systems.
The latest metal 3D printing instruments enable innovative production of structurally strong aluminum and titanium alloy parts while remaining lightweight.
The Future of Automotive Materials: What’s Next?
The automotive materials of tomorrow will unite reduction of weight, environmental sustainability and intelligent features to develop vehicles which represent enhanced safety alongside improved fuel efficiency and protection of the environment.
Fully Recyclable Cars: Auto Manufacturers target to develop automobiles with almost exclusive components of recyclable or biodegradable materials for 2035 production.
Next-Gen Battery Materials: The market shift toward solid-state batteries will trigger automakers to find conductive and lightweight materials that deliver better EV performance.
Graphene & Supermaterials: The strength of graphene enables its use in transforming battery technology as well as coatings and body structures due to its unmatched ability to be highly strong and conductive while flexible.
AI-Integrated Materials: Future materials may include AI sensors and embedded smart coatings that detect structural weaknesses and alert drivers before failures occur.
Conclusion:
Automobile manufacturers seek continuous advancement through material development in order to reach innovation excellence by creating safe vehicles while prioritizing sustainability. Designs of present-day automobiles required every advancement in steel and aluminum and carbon fiber and smart materials to reach their current state.
Evaluations of electric and autonomous mobility require materials to exhibit lightweight capabilities and environmentally-friendly nature and design adaptability. The present directions in the industry result in revolutionary car developments which improve sustainability while maintaining performance standards.

The Impact of Digitalization on the Automotive Industry
The roar of the engine is no longer the only sound defining the automotive industry. A quieter, yet profoundly more powerful force is at play: digitalization. This isn’t just about adding touchscreens to dashboards; it’s a fundamental re-engineering of how vehicles are conceived, designed, built, sold, driven, and maintained. From the initial spark of an idea in a virtual design studio to the intricate dance of robots on the assembly line and extending throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle on the road, digital technology is the new engine driving innovation, efficiency, and transformation. We’re moving beyond mere transportation into an era of intelligent mobility, shaped by data, connectivity, and artificial intelligence. Let’s explore the multifaceted impact of this digital revolution.
Redefining the Vehicle: Connected Cars and the Internet of Things (IoT)
At the heart of this transformation lies the concept of the connected car. Modern vehicles are rapidly evolving into sophisticated mobile platforms, teeming with sensors, processors, software, and advanced communication capabilities. This intricate web, powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), allows vehicles to perceive their environment, communicate with other vehicles (V2V), infrastructure (V2I), pedestrians (V2P), and cloud-based networks (V2X).
This constant data stream unlocks a wealth of possibilities:
- Enhanced Safety: Real-time data sharing enables advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like collision avoidance, adaptive cruise control, and lane-keeping assist. V2X communication provides warnings about road hazards, traffic conditions, or emergency vehicles beyond the driver’s line of sight.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors continuously monitor the health of critical components. By analyzing this data, algorithms can predict potential failures before they occur, alerting drivers or service centers and reducing unexpected breakdowns and maintenance costs. IoT solutions enable tracking of location, fuel levels, and other vital statistics.
- Personalized Experiences: Connected services tailor the in-car environment, offering customized infotainment, navigation synced with personal calendars, and comfort settings adjusted to driver preferences. Over-the-air (OTA) software updates continuously improve functionality and add new features long after the car has left the showroom.
- Data-Driven Insights: For manufacturers, the data collected from connected vehicles is invaluable. It provides deep insights into real-world vehicle performance, usage patterns, component durability, and customer behavior, informing future design, engineering, and service strategies.
The Smart Factory: Manufacturing Reimagined
Digitalization isn’t confined to the vehicle itself; it has profoundly reshaped the factory floor. The principles of Industry 4.0 are being embraced, merging physical production processes with smart, digital technologies:
- Automation and Robotics: Advanced robotics, often guided by AI, perform tasks with greater precision, speed, and consistency than ever before. This includes welding, painting, assembly, and complex quality control inspections.
- AI and Big Data Analytics: AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of production data to includeoptimize workflows, predict equipment failures (predictive maintenance for machinery), and identify bottlenecks. Machine learning models improve quality control by detecting subtle defects that might escape human inspection. Data analytics helps optimize supply chain logistics, ensuring parts arrive just in time and minimizing inventory costs. Leading manufacturers leverage robust data platforms to analyze sensor data for risk assessment and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
- Digital Twins: Creating virtual replicas of production lines and even entire factories allows manufacturers to simulate changes, test new processes, and optimize layouts in a risk-free digital environment before implementing them physically. This accelerates innovation and reduces the costs associated with physical trial-and-error.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): This technology enables rapid prototyping and the production of complex, customized parts on demand, streamlining development and offering new design possibilities.
This smart manufacturing approach leads to increased efficiency, reduced waste, higher product quality, faster production cycles, and greater flexibility to adapt to changing market demands.
Accelerating the Electric Revolution
The global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is inextricably linked with digitalization. Digital technologies are critical across the EV ecosystem:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Sophisticated software monitors and manages battery health, optimizing charging and discharging cycles to maximize range and lifespan. IoT solutions allow remote monitoring of battery parameters.
- AI-Optimized Performance: AI plays a crucial role in optimizing energy consumption based on driving patterns, terrain, and traffic conditions [cite: 11, 4.1]. It can also optimize charging schedules to take advantage of lower electricity rates or periods of high renewable energy generation, reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Charging Infrastructure: Digital platforms manage the network of charging stations, enabling drivers to locate available chargers, reserve spots, and manage payments seamlessly through mobile apps. Smart charging solutions help balance grid load.
- Development and Simulation: Digital tools, including simulation software and virtual testing, significantly accelerate the design and validation process for new EV models and battery technologies, reducing reliance on costly physical prototypes.
Digitalization not only makes EVs more efficient and user-friendly but also helps optimize their integration into the broader energy grid, contributing to decarbonization efforts.
Transforming the Customer Journey
Digital technology is reshaping how customers interact with automotive brands throughout the entire ownership lifecycle:
- Digital Retail: Online configurators, virtual showrooms using Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), and digital purchasing platforms offer a more personalized, convenient, and immersive buying experience. Brands can leverage data analytics to understand customer preferences and offer tailored recommendations and financing options.
- Personalized In-Car Experience: As mentioned, connectivity allows for highly personalized infotainment, navigation, and comfort settings. Voice assistants and intuitive interfaces create a more seamless interaction between the driver and the vehicle.
- Proactive Service and Maintenance: Predictive maintenance alerts and the ability to schedule service appointments via apps or the vehicle’s interface simplify upkeep. OTA updates provide software enhancements and bug fixes remotely, reducing the need for dealership visits. Customer care contact centers utilize digital tools for faster, more intelligent inquiry resolution.
- Building Relationships: Digital channels enable ongoing communication between brands and owners, offering personalized content, loyalty rewards, and support, fostering stronger customer relationships long after the initial sale. Big data insights help understand and acquire customers through personalized marketing.
Enhancing Sustainability and Supply Chain Resilience
Beyond the vehicle and factory, digitalization contributes to broader industry goals:
- Sustainable Operations: Data analytics helps optimize energy consumption in manufacturing plants, reduce waste through smarter material usage, and track the carbon footprint across the value chain. Digital tools enable better simulation and design for lightweighting and aerodynamics, improving vehicle efficiency.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Real-time tracking and data analysis provide greater visibility into complex global supply chains. This allows for better demand forecasting, optimized logistics, reduced inventory holding, and quicker responses to disruptions, enhancing overall resilience and efficiency. Digital solutions improve communication between manufacturers, suppliers, and logistics providers.
Navigating the Digital Challenges
Despite the immense potential, the path to full digitalization is fraught with challenges that the industry must actively address:
- Cybersecurity: As vehicles become more connected and reliant on software, they become attractive targets for cyberattacks. A breach could compromise vehicle control, steal personal data, or disrupt critical functions, posing significant safety risks. Securing the vehicle itself, the communication networks, and the backend servers is paramount. The complexity of the modern supply chain, involving numerous suppliers and interconnected systems, creates multiple potential entry points for attackers.
- Data Privacy and Security: Connected cars generate vast amounts of data, including location, driving behavior, and personal preferences. Ensuring this data is collected, stored, and used ethically and securely, in compliance with regulations like GDPR, is crucial for maintaining consumer trust [cite: 33, 8.1]. Clear policies on data ownership and usage are essential.
- Complexity and Integration: Integrating new digital systems with existing legacy infrastructure can be complex and costly. Ensuring interoperability between systems from different suppliers and managing the sheer volume of software involved requires sophisticated integration strategies.
- Skills Gap: The industry requires a workforce with new skill sets in software development, data science, AI, and cybersecurity. Bridging this skills gap through training, reskilling, and attracting new talent is vital for continued innovation.
- Standardization and Regulation: Clear, consistent standards and regulations are needed globally for aspects like V2X communication protocols, autonomous vehicle testing and deployment, data formats, and cybersecurity requirements [cite: 37, 38, 39, 7.1]. Regulatory uncertainty can hinder investment and slow down progress. Adherence to standards like ISO 27001, TISAX, and UNECE WP.29 is becoming increasingly important.
- Implementation Costs: Significant investment is required to implement new digital technologies, upgrade infrastructure, and retrain the workforce.
The Road Ahead: An Intelligent, Evolving Landscape
The digitalization of the automotive industry is not a destination but an ongoing journey. We are witnessing a paradigm shift towards software-defined vehicles (SDVs), where functionality and value are increasingly determined by software rather than hardware alone. Future advancements in AI, edge computing, 5G/6G connectivity, and quantum computing will continue to push the boundaries.
We can anticipate
- Higher Levels of Autonomy: Continued progress in sensor technology, AI, and validation methods will lead to increasingly sophisticated autonomous driving capabilities, potentially transforming personal mobility, logistics, and urban planning.
- New Mobility Services: Digital platforms will further enable the growth of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS), integrating various transport options (ride-sharing, public transit, micro-mobility) into seamless, on-demand services.
- Circular Economy Integration: Digital tracking and data management will play a key role in managing the lifecycle of vehicles and components, particularly batteries, facilitating reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling.
- Hyper-Personalization: Deeper integration of AI and data analytics will allow for vehicles and services that adapt even more precisely to individual user needs and preferences in real time.

Urban Mobility: The Sustainable Future of City Transportation
With rapid urban growth worldwide, sustainable transportation is no longer optional—it’s essential. City mobility impacts quality of life, the environment, and city function. As climate change, congestion, and overcrowding intensify, we must transform transportation into a sustainable, efficient, and universally accessible system.
What is Sustainable Urban Mobility?
Sustainable urban mobility refers to transportation systems that minimize environmental impact, reduce energy consumption, and improve urban life. It focuses on public transport, non-motorized options like walking and cycling, electric vehicles (EVs), and shared mobility solutions. The goal is to reduce carbon emissions, promote healthier lifestyles, and ensure accessibility for all, regardless of socioeconomic background.
The Expanding Horizon of Sustainable Urban Mobility: Addressing the Multifaceted Challenges of Tomorrow’s Cities
The relentless march of urbanization presents a complex tapestry of opportunities and challenges, with urban mobility standing as a critical thread woven through its fabric. The ease, efficiency, and environmental impact of how people and goods move within and around cities profoundly influence economic prosperity, social equity, public health, and overall quality of life. Today, many urban centers grapple with a burgeoning mobility crisis, characterized by persistent traffic congestion, suffocating air pollution, limited access for vulnerable populations, and an infrastructure struggling to keep pace with evolving needs. Understanding the intricate web of these issues is paramount to charting a course towards a more sustainable and equitable urban future.
Deconstructing the Urban Mobility Crisis: A Multifaceted Challenge
The current state of urban mobility in many parts of the world is far from ideal, demanding urgent and comprehensive solutions. The key challenges that define this crisis are deeply interconnected and require a holistic approach to address effectively.
- The Grip of Traffic Congestion:
Traffic congestion has become an almost ubiquitous feature of modern urban life. The daily grind of gridlock not only steals precious time from individuals, impacting productivity and personal well-being, but also carries significant economic and environmental costs. Idling vehicles guzzle fuel inefficiently, leading to increased expenditure for commuters and businesses alike. Furthermore, the prolonged periods of engine operation in congested areas contribute significantly to air pollution and the emission of greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change. The economic ramifications extend beyond fuel consumption, impacting supply chains, delivery times, and overall business efficiency. The frustration and stress associated with daily commutes also take a toll on mental health and social cohesion.
- The Suffocating Burden of Air Pollution and Emissions:
The reliance on gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles as the dominant mode of urban transportation has had a devastating impact on air quality. Cities around the globe are battling alarming levels of pollutants such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants pose severe risks to public health, contributing to respiratory illnesses like asthma and bronchitis, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to the harmful effects of air pollution. Beyond the immediate health consequences, vehicle emissions are a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, driving climate change and its associated impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems.
- The Divide in Access to Transportation:
Equitable access to transportation is a fundamental pillar of a just and inclusive society. However, in many urban areas, significant disparities exist, leaving low-income neighborhoods and marginalized communities with limited affordable and efficient mobility options. This lack of access can create significant barriers to employment, education, healthcare, and social participation, perpetuating cycles of poverty and inequality. When transportation options are inadequate or unaffordable, residents in these areas face longer commute times, increased transportation costs, and reduced opportunities for economic advancement and social integration. Addressing this accessibility gap is crucial for fostering social equity and ensuring that all urban residents can participate fully in the life of the city.
- The Lagging Infrastructure Deficit:
The transition towards sustainable urban mobility requires a fundamental shift in infrastructure planning and investment. Many cities today lack the essential infrastructure necessary to support and encourage sustainable transit modes. This includes a scarcity of dedicated cycling lanes and pedestrian walkways, making active mobility unsafe and unappealing. The inadequate deployment of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations acts as a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of zero-emission vehicles. Furthermore, outdated or poorly maintained public transportation infrastructure can lead to inefficiencies, delays, and a less attractive user experience. Investing in and modernizing urban infrastructure to prioritize sustainable modes of transport is a prerequisite for achieving long-term mobility goals.
The Pillars of Sustainable Urban Mobility: A Collaborative Approach
Moving beyond the current crisis necessitates a concerted effort involving technological innovation, forward-thinking policy frameworks, and a shift in individual and societal behaviors. The key components of sustainable urban mobility provide a roadmap for this transformation.
- The Backbone of Robust Public Transportation:
A well-functioning and attractive public transportation system forms the cornerstone of sustainable urban mobility. Efficient buses, subways, trams, and light rail networks can significantly reduce the reliance on private vehicles, leading to decreased congestion and emissions. To maximize their effectiveness, these systems must be reliable, affordable, accessible, and convenient. The integration of smart ticketing systems, real-time tracking information, and comfortable, modern vehicles enhances the user experience and makes public transport a more appealing alternative to private cars. Strategic investment in expanding and modernizing public transportation networks is crucial for accommodating growing urban populations and fostering a shift towards shared mobility.
- The Electrification Imperative: Embracing Electric Vehicle Adoption:
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) represents a crucial step towards cleaner urban air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Zero-emission EVs, powered by increasingly renewable energy sources, offer a pathway to decarbonize the transportation sector. However, widespread EV adoption requires a supportive ecosystem, including an expanded and readily accessible charging infrastructure. Governments and private sector players must collaborate to deploy charging stations in residential areas, workplaces, public spaces, and along major transportation corridors. Incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, can further accelerate the adoption of EVs by making them more affordable. Furthermore, the electrification of public transportation fleets, including electric buses and trains, will significantly contribute to reducing emissions from the public sector.
- Empowering Active Mobility: Prioritizing Pedestrians and Cyclists:
Promoting active mobility, such as walking and cycling, offers a multitude of benefits for individuals and cities. Creating pedestrian-friendly streets with safe and accessible sidewalks encourages walking for short distances, improving physical activity and reducing reliance on motorized transport. The development of dedicated and well-maintained bike lanes and networks makes cycling a safer and more attractive option for commuting and leisure. Bike-sharing and e-scooter programs provide convenient and affordable options for short-distance travel, further encouraging active mobility. Investing in infrastructure that prioritizes pedestrians and cyclists not only improves public health and reduces congestion but also contributes to creating more vibrant and livable urban environments.
- The Power of Sharing: Leveraging Shared Mobility Platforms:
Shared mobility platforms, including car-sharing, ride-hailing, and bike-sharing services, offer the potential to optimize vehicle utilization and reduce the overall number of private vehicles on urban roads. These services can provide cost-effective and flexible transportation options, particularly for individuals who do not own a car or for specific trip needs. However, it is crucial to ensure that these platforms are integrated with the broader public transportation network and are regulated to avoid exacerbating congestion or negatively impacting labor standards. When implemented strategically, shared mobility can complement public transport and active mobility, offering a comprehensive suite of sustainable transportation choices.
- The Synergy of Integration: Building Interconnected Networks:
The true potential of sustainable urban mobility is realized when different transport modes are seamlessly connected and easily accessible. Integrated networks, facilitated by smart city technologies, enhance the user experience and minimize the need for private car ownership. This includes unified ticketing systems that allow passengers to easily switch between buses, trains, and shared mobility options. Real-time information on public transport schedules, traffic conditions, and available shared mobility options, accessible through mobile applications and digital displays, empowers users to make informed travel decisions. Smart traffic management systems can optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and prioritize public transport vehicles. The integration of these technologies and services creates a cohesive and user-friendly mobility ecosystem that encourages the adoption of sustainable transportation choices.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Embracing Sustainable Urban Mobility
The transition towards sustainable urban mobility yields a wide array of benefits that extend far beyond simply alleviating traffic congestion. These benefits positively impact individuals, communities, and the environment.
- A Greener Future: Mitigating Environmental Impact:
Reducing our reliance on fossil fuels in the transportation sector is paramount for mitigating climate change and improving air quality. The shift towards electric vehicles and the promotion of public and active mobility significantly cut greenhouse gas emissions and noise pollution, creating cleaner, quieter, and healthier urban environments. This contributes to a more sustainable future for generations to come.
- Health and Well-Being: Fostering a Healthier Population:
Encouraging walking and cycling as modes of transportation directly promotes physical activity, leading to improved cardiovascular health and reduced rates of obesity and related diseases. Cleaner air, resulting from reduced vehicle emissions, lowers the incidence of respiratory illnesses. Furthermore, reducing traffic congestion can alleviate stress and improve mental well-being, contributing to a higher quality of life for urban residents.
- Economic Advantages: Driving Growth and Savings:
Sustainable transportation options can lead to significant cost savings for individuals and governments. Public transportation, cycling, and shared mobility services are often more affordable than owning and maintaining a private vehicle. Reduced traffic congestion translates to lower fuel consumption and increased productivity for businesses. Government investment in green transportation infrastructure can stimulate economic growth by creating jobs in manufacturing, technology, and public transit operations. Furthermore, a healthier population, resulting from improved air quality and increased physical activity, can lead to lower healthcare costs.
- Enhanced Livability: Creating More Desirable Cities:
Cities that prioritize sustainable urban mobility become more livable and attractive places to reside. Less congestion creates more efficient and enjoyable commutes. Cleaner air improves public health and the overall quality of life. The development of green spaces, pedestrian-friendly streets, and vibrant public areas enhances the urban fabric and fosters a stronger sense of community. Improved transport accessibility ensures that all residents can participate fully in the economic, social, and cultural life of the city.
- Economic Opportunities: Fueling Innovation and Job Creation:
The transition to sustainable urban mobility creates new economic opportunities and drives innovation across various sectors. The burgeoning electric vehicle industry, including manufacturing, charging infrastructure development, and battery technology, is a significant source of job creation. The development and implementation of smart traffic management systems, public transit technologies, and shared mobility platforms also generate employment and foster technological advancements. Investing in sustainable transportation solutions can position cities as leaders in the green economy, attracting investment and talent.
The Road Ahead: A Call for Integrated Action
Sustainable urban mobility is not merely an aspiration but an essential imperative for the future of our cities. As urbanization continues its rapid pace, the challenges posed by traffic congestion, air pollution, and inequitable access will only intensify if left unaddressed. The path forward requires a holistic and integrated approach that embraces technological innovation, implements supportive policy frameworks, and fosters behavioral shifts towards more sustainable transportation choices.
By prioritizing robust public transportation systems, accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles, promoting active mobility, strategically leveraging shared mobility platforms, and building interconnected and intelligent transportation networks, we can transform our cities into more navigable, healthier, and desirable places to live. This transition demands collaboration between governments at all levels, the private sector, research institutions, and individual citizens. It requires long-term vision, strategic investment, and a commitment to creating equitable and efficient transportation systems that serve the needs of all urban residents while safeguarding the environment for future generations. The journey towards sustainable urban mobility is a continuous one, but it is a journey that promises a brighter, more sustainable, and more livable future for our cities.

The Future of Car Safety: How Smart Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) Are Saving Lives
Have you ever had that gut-wrenching part of your life, where the guy in front of you comes to an abrupt stop? Just a momentary distraction or lapse in attention — maybe a check of the phone, an adjustment of the radio or just zoning out for a few seconds — can turn an ordinary drive to a potential disaster. But what if your car had a second set of eyes to help you avoid these kinds of accidents? The advent of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) is transforming the landscape of automotive safety, propelling car safety to unparalleled heights by preventing accidents and preserving human lives.
In this blog, we will discuss how ADAS is transforming car safety, its core features, real-world impacts, limitations, and its potential
The Rise of ADAS: A Revolution in Vehicle Safety
ADAS technology has established a groundbreaking period in automotive security systems. Vehicle systems designed through intelligence offer assistance to drivers to make safer choices while decreasing the occurrence of accidents and reducing negative outcomes and providing backup when necessary. ADAS systems use sensors as well as cameras and radar and lidar to track the external environment of the vehicle so drivers receive alerts or when necessary they take over control to avoid crashes. The advancement of ADAS has been extraordinary since it started with fundamental safety components such as seatbelt reminders and grew into systems which can both steer and brake and control vehicle operations. The current automotive safety technology of ADAS operates as a protective system which decreases accidents while making streets safer to use.
From Passive To Executive: The Development of ADAS
ADAS technologies were mainly reactive at first since they could only warn about an existing danger. But now, with technological development, ADAS has the potential to be proactive by preventing accidents before they happen.
The Potency of Sensor Fusion: Enhanced Precision and Efficiency in Systems
Sensor fusion is one of the most notable developments in the advance of ADAS. By integrating data from all other sensors: cameras, radar, lidar, etc, ADAS capture richer details about the environment surrounding the vehicle. This fusion makes the entire system smarter enabling it to act faster during emergency cases.
For instance, a camera detects pedestrians or a vehicle, or a road sign, and radar gauges the speed of the vehicle. All of these sensors working together paint a clearer image of what is on the road and enables ADAS to respond quickly and efficiently to a threat.
Predictive Safety Features: Proactively Looking To Avoid Accidents
The integration of aviation technology into vehicles has come a long way and one of the latest technologies to spring forth from this is forward collision avoidance systems, which are among new instituted and predictive safety components .Predictive safety features are one of the most innovative advancements in ADAS technologies. Predictive systems do not only counter immediate threats, they also actively analyzedriving styles and road conditions to predict future dangers. If the system spots an increased number of lane changes and abrupt braking velocities, it could predict a car cutting across your lane and brace itself for such an event.
Analyzing this data, predictive systems are able to take action such as steering away from a possible collision before the driver has had any time to react. This kind of approach also raises the overall safety of the roads by assisting in the prevention of accidents at their very root.
The Effects of ADAS – Lesser Accidents and Minimal Damage
ADAS has had a definitive effect on reduction of accidents and enhancement of road safety. Studies indicate time and again that there is better road safety with ADAS equipped vehicles because such vehicles are involved in accidents less often, and when they do get into accidents, they are not as tragic.
Stats Are Accurate: Benefits In Society Are Evident
The IIHS have remarked that AEB all by itself has proven to cut rear collisions as much as 50% and lane shifts might get as high as 20%. ADAS equipped cars saw a boost in insuraceclaims due to reduced accident frequency and severity caused by the systems.
The data demonstrates how ADAS is more than a hypothetical safety system. It is a life-saving device that lowers expenses for attained due to road accidents.
Practical Illustrations: Real Example of An Advanced Driver Assistance System Operation
In the practical field, such as automobile rear-end collisions, autonomous emergency braking (AEB) systems instantly stop the vehicle if the driver does not respond in time. Also, lane keeping assistance (LKA) adopters no longer have to deal with unintended head-on collisions because it helps restrain drivers from subsequently drifting. Such studies are evidence that ADAS works optimally in real life.
Final Thoughts: Future Developments in ADAS and Vehicle Safety Technologies
Preventative and mitigative crash medical care measures such as ADAS technologies have been effective in saving lives already. As we transition towards more developed systems and autonomous vehicles, there will be continued improvement in safety. We should also not forget that these systems are meant to support drivers, not do the task for them. Drivers must also stay aware, know what the vehicle can do, and participate in the basic fundamentals of driving.
ADAS will further develop and enhance safety, efficiency, and functionality in driving and set the stage for the next age of vehicle automation. The future is positive, all because of the safety technology innovations we’ve received through ADAS.

The Role of Robotics in Modern Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry has long been a pioneer in adopting new technologies to improve efficiency, safety, and quality. In recent years, robotics has become an integral part of modern car manufacturing, revolutionizing traditional assembly processes and redefining industry standards.
From precision welding to AI-driven quality control, robots have transformed how vehicles are built, making production lines faster, safer, and more reliable. But what exactly makes robotics such a crucial component in automotive manufacturing? This blog explores the impact of robotics, its key applications, and the future of automation in the industry.
The Evolution of Robotics in Automotive Manufacturing
Traditionally, car manufacturing relied heavily on manual labor, with workers assembling various components by hand. While effective, this process was time-consuming and prone to human error. The introduction of robotics in the late 20th century marked a turning point, enabling manufacturers to automate repetitive tasks, increase precision, and reduce production time.
Initially, robots were limited to basic functions such as welding and painting. However, advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technology have significantly expanded their capabilities. Today, robotics plays a critical role in nearly every stage of vehicle production, from assembling complex components to conducting final quality inspections.
How Robotics is Transforming Automotive Manufacturing
- Enhanced Precision and Quality
One of the most significant advantages of robotics is its ability to perform tasks with unparalleled accuracy. Robots equipped with advanced sensors and AI-driven software ensure that every component is assembled to exact specifications. This level of precision minimizes defects, reduces waste, and enhances overall product quality.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Unlike human workers, robots can operate continuously without breaks, significantly boosting production rates. Automated systems streamline manufacturing processes, allowing companies to meet growing consumer demand without compromising quality.
- Improved Workplace Safety
Automotive manufacturing involves several hazardous tasks, such as welding, heavy lifting, and exposure to toxic chemicals. By automating these high-risk processes, robotics helps create a safer work environment, reducing workplace injuries and improving overall employee well-being.
- Cost Reduction and Sustainability
While the initial investment in robotic technology can be substantial, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. Robots optimize material usage, minimize waste, and reduce errors that could lead to expensive recalls. Additionally, robotic automation supports sustainability initiatives by improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
- Predictive Maintenance and Smart Manufacturing
Modern robotics, integrated with artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), enables predictive maintenance—identifying potential equipment failures before they occur. By analyzing real-time data, manufacturers can schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted production.
Key Applications of Robotics in the Automotive Industry
- Robotic Welding
Welding is a fundamental process in car manufacturing, and robotic welders provide superior precision, strength, and consistency. These automated systems ensure that every weld meets stringent quality standards, enhancing the structural integrity of vehicles.
- Automated Painting and Coating
Robotic painting systems deliver a flawless, uniform finish while reducing paint waste and harmful emissions. This level of consistency enhances the aesthetic appeal and longevity of vehicles.
- Assembly Line Automation
From installing seats and dashboards to securing nuts and bolts, robotic systems handle intricate assembly tasks with high accuracy. This automation speeds up production while maintaining product quality.
- Quality Control and Inspection
Vision-based robotic systems use high-resolution cameras and AI algorithms to detect even the smallest defects. By identifying issues early in the production process, manufacturers can prevent costly rework and ensure that only top-quality vehicles reach consumers.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate in isolation, collaborative robots (or “cobots”) work alongside human employees. These intelligent systems assist with tasks that require both precision and adaptability, improving overall workflow efficiency.
The Future of Robotics in Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry is rapidly evolving, and robotics will continue to play a central role in shaping its future. Innovations in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT connectivity will further enhance automation, making production lines smarter and more adaptable.
In the coming years, we can expect:
– Greater AI Integration: Smarter robots capable of self-learning and real-time decision-making.
– Fully Automated Factories: Production facilities with minimal human intervention, leading to even faster and more efficient manufacturing.
– Sustainability Improvements: Robotics-driven processes that reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
While automation will continue to advance, the role of human workers remains crucial. Engineers, designers, and technicians will be needed to oversee robotic operations, develop new technologies, and ensure the seamless integration of automation with human expertise.
Conclusion
Robotics has undeniably transformed modern automotive manufacturing, enhancing efficiency, precision, and safety. As technology continues to evolve, manufacturers that embrace robotics and AI-driven automation will gain a competitive edge in producing high-quality vehicles at a faster pace and lower cost.
The road ahead is one of innovation and progress, where robotics and human ingenuity work together to drive the future of automotive manufacturing.
What are your thoughts on the role of robotics in car production? Share your insights in the comments below!

How to Expand Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure in 5 Game-Changing Steps
Want to see more EVs on the road? The secret is simple: Better charging networks.
The growth of electric vehicles on roads faces a primary obstacle because there are few places to charge them. People will be reluctant to adopt electric vehicles unless they discover charging facilities that combine speed along with affordability and reliability.
The good news? We can fix this.
An innovative expansion of electric vehicle charging stations will remove driving concerns while speeding up charging capability to make electric cars the preferred option for many motorists. The following discussion will outline five transformational steps necessary for establishing a future-proof EV charging network.
Step 1: Find the Best Locations for Maximum Impact
You wouldn’t open a gas station in the middle of nowhere, right? EV chargers need the same strategic placement to be useful.
How to do it:
Target High-Traffic Areas – The parking pattern of extended durations exists in shopping malls and business districts together with apartment complexes.
Expand Highway Coverage – Highway travels become a nightmare when there are no dependable rapid charging stations available.
Close the Rural Gap – Access problems in rural areas persist whereas city drivers have various transportation alternatives. Fixing this situation remains important.
Think Workplaces & Fleets – The increasing popularity of electric fleets opens up an opportunity for companies to install charging services at their office sites and depot areas.
Why it matters: EV usage increases dramatically while revenue expansion and faster EV market adoption occurs when charging stations get situated in strategic locations.
Step 2: Get the Money Flowing—From the Right Sources
EV chargers aren’t cheap. A high-speed DC fast charger can cost over $100,000 to install. The trick? Make someone else pay for it.
How to fix it:
Tap into Government Grants & Tax Credits – The entire world is spending billions of dollars to develop charging infrastructure networks. Take advantage!
Partner with Big Brands – The investments in charging infrastructure by big companies like Starbucks and Walmart along with Tesla should gain your support.
Offer Subscriptions & Membership Plans – Just like Netflix, EV drivers love convenience —give them easy access to charging for a monthly fee.
Encourage Retail & Business Owners – A charging station installation strengthens commercial activity by attracting additional visitors who extend their period of stay.
Why it matters: Existing funding availability makes it possible for charging network infrastructure to scale up at a high rate without financial strain.
Step 3: Make Charging Faster—Because No One Likes to Wait
Let’s be real—nobody wants to wait hours to charge their car. The solution? Ultra-fast, next-gen charging tech.
How to do it:
Deploy 150 kW+ Fast Chargers – According to EV standards the Tesla Model Y and Hyundai Ioniq 5 reach 80% charging capacity in less than 20 minutes which should become standard for the industry.
Adopt 800V Charging Systems – The innovative technology enables brands to reduce charging periods to only 10 minutes.
Invest in Wireless Charging – Drivers of future EVs will obtain charging capability by simply parking over a charging pad instead of traditional cable-based charging.
Keep Up With Battery Innovations – When solid-state batteries become commercially available they will achieve five times faster charging speeds compared to existing lithium-ion packs thus requiring ready stations.
Why it matters: Faster charging means happier customers, shorter wait times, and fewer stations needed to serve more EVs.
Step 4: Make Charging Green & Smart (Because the Grid Needs It)
More EVs = More electricity demand. The absence of planning before implementation leads to power grid susceptibility to failure. Renewable energy coupled with smart grid systems provide the solution.
How to fix it:
Use Solar & Wind Energy – Charging stations powered by solar panels or wind turbines reduce grid dependence.
Store Excess Energy in Batteries – The system function of Tesla’s Megapacks parallels energy storage because it deals with demand spikes while reducing operational costs.
Enable Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Tech – Under high demand scenarios vehicles with electric power systems act as grid power suppliers to avoid power outages.
Use AI for Smart Charging – Smart network infrastructure controls the time of charging to both minimize power grid pressure and decrease expenses.
Why it matters: Sustainable charging is a win-win for the environment, the power grid, and EV owners.
Step 5: Make Charging Easy, Accessible & Fun
A charging station that is practical to locate has user-friendly operations and places customers first should be considered the best.
How to do it:
Create a Mobile App – Drivers should be able to find, book, and pay for charging with a few taps.
Improve Station Uptime & Maintenance – Nothing is worse than pulling up to a broken charger—regular upkeep is key.
Standardize Connectors – A charging station that is practical to locate has user-friendly operations and places customers first should be considered the best.
Make Charging Accessible for Everyone – Stations should be designed for all drivers, including those with disabilities.
Why it matters: A smooth, hassle-free charging experience will turn more people into EV believers.
Final Thoughts: The Road Ahead for EV Charging
Electric vehicles moved beyond the status of alternatives because they have become the primary transport mode of the future. However, their widespread adoption hinges on the development of a fast, reliable, and accessible charging infrastructure. The placement of charging stations at crucial locations through funding from both government and private sectors combined with swift charging innovations and renewable power solutions and advanced UI will remove charging stress making electric vehicles convenient for everyone. Electric mobility transitions are already taking place so the only task before us is to construct the necessary infrastructure speedily. A new clean transportation system will replace gas stations when we correctly build the necessary infrastructure since clean efficient transportation systems will set new performance standards. The time has arrived to accelerate the future development process because we need to start making this transformation succeed.
The future is electric. The faster we build a reliable, accessible, and sustainable EV charging network, the sooner we can leave gas stations in the past.

The Rise of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
Introduction
In the modern world, where technology is rapidly transforming transportation, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication is emerging as a crucial innovation. V2X is a technology that enables vehicles to interact with their surroundings, including other vehicles, infrastructure, pedestrians, and cloud-based networks. By facilitating real-time data exchange, V2X aims to improve road safety, optimize traffic management, and enhance transportation efficiency.
With the rise of autonomous driving, 5G connectivity, and smart cities, V2X technology is becoming increasingly essential. Governments and automotive manufacturers worldwide are investing heavily in intelligent transport systems to create a safer and more efficient road network. According to industry reports, V2X technology can reduce traffic accidents by up to 80 percent by providing early warnings about hazards, enabling vehicles to react to dangers before they become critical.
This blog explores the components of V2X communication, its impact on road safety and traffic efficiency, its environmental and economic benefits, the challenges it faces, and the future of this transformative technology.
1. Understanding V2X Communication
What is V2X?
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) is an advanced communication system that allows vehicles to share real-time data with various elements in their environment. This technology is designed to support safer and more efficient transportation by creating a fully connected driving ecosystem.
Types of V2X Communication
V2X communication is categorized into four major types:
a) Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication
V2V communication enables vehicles to exchange critical data such as speed, location, and braking activity. The key benefits include:
- Collision prevention: Vehicles alert each other about sudden braking or lane changes.
- Cooperative driving: Cars can synchronize movement, reducing traffic congestion.
- Blind spot alerts: Vehicles warn drivers of obstacles in hard-to-see areas.
b) Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Communication
V2I communication connects vehicles to road infrastructure like traffic lights, toll booths, and parking systems. This helps in:
- Traffic signal optimization: Smart traffic lights adjust based on real-time traffic flow.
- Road condition warnings: Vehicles receive alerts about construction zones, icy roads, or accidents ahead.
- Automatic toll payment: Reducing delays and congestion at toll stations.
c) Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P) Communication
V2P enhances pedestrian safety by allowing vehicles and pedestrians to communicate through mobile apps, wearables, and smart crosswalks.
- Pedestrian alerts: Vehicles detect nearby pedestrians and provide warnings.
- Crosswalk safety: Smart signals adjust based on pedestrian movement.
- Bicycle awareness: Cyclists can be detected, reducing collision risks.
d) Vehicle-to-Network (V2N) Communication
V2N connects vehicles to cloud-based services, navigation systems, and traffic control centers. This provides:
- Real-time traffic updates: Vehicles receive alternate route suggestions to avoid congestion.
- Weather alerts: Drivers are warned about hazardous conditions like fog, storms, or ice.
- Remote diagnostics: Vehicles receive maintenance alerts before potential breakdowns.
2. The Role of V2X in Road Safety
Road safety is one of the most critical benefits of V2X communication. Studies suggest that human error accounts for over 94 percent of traffic accidents, and V2X can significantly reduce these incidents.
How V2X Enhances Road Safety
- Collision avoidance: Vehicles exchange data to prevent crashes by issuing early warnings.
- Intersection safety: V2I communication prevents accidents at busy junctions by alerting drivers to red lights and stop signs.
- Emergency vehicle priority: Ambulances and fire trucks communicate with traffic signals for uninterrupted movement.
- Weather and road alerts: V2X-enabled vehicles receive real-time warnings about road hazards, such as icy roads or sudden lane closures.
By integrating V2X communication into everyday driving, road fatalities and injuries can be drastically reduced.
3. Traffic Efficiency and Congestion Reduction
Traffic congestion remains a major issue in urban areas, leading to longer commute times, fuel wastage, and increased air pollution. V2X communication plays a crucial role in reducing congestion and improving traffic flow.
How V2X Helps Reduce Traffic Congestion
- Smart traffic lights: Adjust signal timings based on real-time vehicle density.
- Dynamic rerouting: Vehicles receive real-time navigation updates to avoid bottlenecks.
- Platooning for autonomous vehicles: Vehicles traveling in groups optimize speed and distance to improve road capacity.
By enabling vehicles and infrastructure to work together, V2X reduces unnecessary stops, idling, and delays, resulting in more efficient road networks.
4. Environmental and Economic Benefits
In addition to safety and traffic efficiency, V2X communication offers substantial environmental and economic advantages.
Environmental Benefits
- Lower emissions: Reduced congestion means fewer carbon emissions.
- Fuel efficiency: Vehicles optimize speed and braking, leading to lower fuel consumption.
- Better EV integration: Electric vehicles use V2X to find charging stations and optimize battery life.
Economic Benefits
- Lower infrastructure costs: Smarter traffic management reduces the need for costly road expansions.
- Fewer accidents, lower insurance costs: A decrease in accidents leads to lower insurance premiums.
- Increased productivity: Reduced traffic congestion results in more efficient business operations.
By enhancing efficiency and reducing fuel consumption, V2X contributes to both economic growth and environmental sustainability.
5. Challenges and Roadblocks in V2X Adoption
Despite its numerous advantages, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of V2X technology.
a) Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks
- Cyber threats: Vehicles sharing real-time data are vulnerable to hacking.
- Data privacy concerns: Protecting sensitive user information is a major issue.
b) Infrastructure and Cost Challenges
- High implementation costs: Upgrading road infrastructure to support V2X requires significant investment.
- Government and industry collaboration needed: Public and private sector partnerships are crucial for funding and deployment.
c) Standardization Issues
- Lack of global standards: Different countries and automakers use varying protocols, leading to compatibility issues.
- Regulatory challenges: Policies must be developed to ensure seamless V2X integration.
Addressing these challenges is essential to making V2X a universally adopted technology.
6. Future Trends and the Road Ahead
The future of V2X is promising, with advancements in 5G, AI, and autonomous vehicles driving its growth.
Key Trends in V2X Development
- 5G-powered V2X: Faster, more reliable communication for real-time data exchange.
- AI and machine learning integration: Predictive analytics will enhance safety and efficiency.
- Autonomous vehicles: V2X will be crucial for self-driving cars to navigate safely.
- Government regulations: Policies will encourage automakers and cities to adopt V2X technology.
As cities move toward smart mobility solutions, V2X will become an essential component of next-generation transportation systems.
Conclusion
V2X communication is transforming the future of transportation by enhancing road safety, improving traffic flow, and reducing environmental impact. By enabling vehicles to communicate with each other and their surroundings, V2X minimizes accidents, reduces congestion, and lowers emissions.
However, challenges such as cybersecurity risks, infrastructure costs, and standardization issues need to be addressed for widespread adoption. With continuous technological advancements, policy support, and industry collaboration, V2X will play a vital role in shaping the future of mobility.
As we move toward autonomous driving and smart cities, V2X will be the foundation for a safer, more efficient, and more connected transportation ecosystem.
This version maintains clarity, coherence, and depth while ensuring uniform formatting. Let me know if you’d like any further refinements!
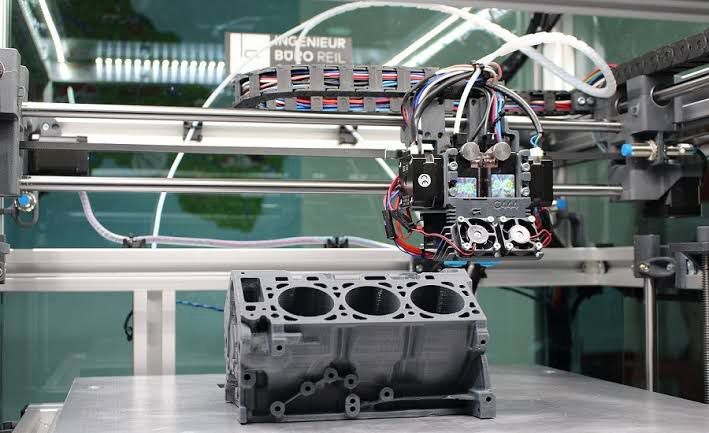
The Potential of Additive Manufacturing in Automotive Production: A Game-Changer?
Introduction
The automotive industry has always been at the forefront of technological innovation, from the assembly line revolution to the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles. Now, another breakthrough is reshaping the way cars are designed and built—Additive Manufacturing (AM), commonly known as 3D printing.
This technology is no longer just a tool for rapid prototyping; it is becoming a core part of vehicle production, enabling manufacturers to create lightweight components, customize designs, and reduce waste like never before. With major automakers like Ford, BMW, and Bugatti already integrating AM into their manufacturing processes, the question arises: Is additive manufacturing the future of automotive production?
The Rise of Additive Manufacturing in Automotive Production
Traditional car manufacturing relies on casting, molding, and machining processes that are time-consuming and material-intensive. Additive manufacturing, on the other hand, builds parts layer by layer using digital designs, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency.
1. Rapid Prototyping and Faster Innovation
One of the earliest and most impactful applications of AM in the automotive sector is prototyping. Engineers can design and print parts within hours instead of weeks, significantly accelerating research and development cycles.
- Ford has used 3D printing to cut prototyping costs by up to 90%, allowing for faster design iterations and innovation.
- Porsche uses AM for motorsport applications, where quick component testing and modification can provide a competitive edge.
By shortening development timelines, AM is helping automakers bring new models and innovative features to market much faster.
2. Lightweight Components: Enhancing Performance and Efficiency
Reducing vehicle weight is a top priority for manufacturers, as lighter cars offer better fuel efficiency, higher performance, and lower emissions. Additive manufacturing makes it possible to create hollow, lattice-structured, or topology-optimized parts that maintain strength while drastically reducing weight.
- Bugatti introduced a 3D-printed titanium brake caliper, making it 40% lighter than conventional aluminum ones.
- General Motors leveraged AM to develop an optimized seat bracket that is 20% stronger and 40% lighter than its traditionally manufactured counterpart.
For electric vehicles (EVs), weight reduction is even more critical, as lighter batteries and components can extend driving range and improve efficiency.
3. Customization and On-Demand Manufacturing
Mass production has traditionally meant limited customization options for consumers. Additive manufacturing is changing this by enabling on-demand, highly personalized vehicle components.
- BMW’s Mini Yours Customized program allows customers to design and 3D print personalized trim pieces, dashboards, and even door handles.
- Luxury brands are using AM to create one-of-a-kind interior designs, from engraved nameplates to custom gear shifts.
Beyond personalization, on-demand manufacturing is proving to be a game-changer for replacement parts. Instead of keeping massive inventories of spare parts, manufacturers can print components as needed, reducing storage costs and wait times for customers.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting AM
Despite its potential, additive manufacturing still faces hurdles that must be addressed before widespread adoption in full-scale automotive production.
1. High Initial Costs
AM technology, especially for high-performance metal printing, requires expensive machinery and specialized materials. While prices are gradually decreasing, scaling up production remains a challenge for many manufacturers.
2. Material Limitations and Structural Integrity
While AM works well for certain materials like plastics, titanium, and aluminum, not all car parts can yet be effectively 3D printed. Components that require extreme durability, heat resistance, or impact absorption often still rely on traditional manufacturing methods.
3. Regulatory and Safety Concerns
As with any new technology, safety and regulatory approval are critical. For AM-produced parts to be widely accepted, they must meet strict automotive industry standards and undergo rigorous testing to ensure they match or exceed the performance of traditionally manufactured components.
The Hybrid Future: Integrating Additive and Traditional Manufacturing
While additive manufacturing is unlikely to completely replace traditional methods in the near future, the most promising approach is a hybrid model that combines both technologies for maximum efficiency and innovation.
- AM can be used for rapid prototyping, low-volume production, and complex components, while
- Conventional methods remain essential for mass production of structural and high-stress components.
Several automakers are already adopting this hybrid strategy:
- Volkswagen is using AM to produce low-volume production parts while maintaining traditional manufacturing for high-volume components.
- Ford has combined 3D-printed parts with traditional metal casting techniques, creating stronger and lighter structures.
The Road Ahead
The future of automotive production is being reshaped by additive manufacturing. While challenges remain, the benefits—faster innovation, lighter vehicles, customization, and reduced waste—are too significant to ignore.
The industry is moving toward a hybrid approach, blending traditional manufacturing with 3D printing technology to optimize efficiency, cost, and design flexibility. As AM technology advances, we may soon see entire car frames, engines, and even self-healing materials produced using 3D printing.
So, the question isn’t if additive manufacturing will revolutionize automotive production, but how soon will we see fully 3D-printed cars on the roads?

The Importance of Cybersecurity in Connected and Autonomous Vehicles
The automotive industry is experiencing a transformative revolution, propelled by the rapid advancement of connected and autonomous vehicle (CAV) technology. What was once confined to the realm of science fiction is now becoming an integral part of modern innovation, as vehicles evolve into intelligent, self-operating machines capable of communicating with each other and their surroundings. CAVs hold the promise of fundamentally reshaping transportation by delivering enhanced safety, greater efficiency, reduced traffic congestion, and unparalleled levels of convenience. Equipped with an array of sophisticated sensors, cutting-edge artificial intelligence, and seamless communication systems, these vehicles are set to redefine how we perceive and interact with mobility. However, alongside these exciting possibilities comes a critical challenge: the pressing need for robust and resilient cybersecurity measures. As vehicles become increasingly dependent on complex software systems and real-time data exchange, they also become potential targets for cyberattacks that could compromise safety, privacy, and functionality. Ensuring the cybersecurity of CAVs is not just a technical necessity but a foundational requirement for their safe and successful integration into society.
Cybersecurity in the context of connected and autonomous vehicles is far more than just protecting onboard systems from hackers—it is about safeguarding lives, data, and public trust. As CAVs rely heavily on real-time communication with other vehicles (V2V), infrastructure (V2I), and cloud-based platforms, any breach in these communication channels could lead to disastrous consequences, including accidents, traffic disruptions, or unauthorized access to sensitive user information. A malicious actor could manipulate navigation systems, disable safety features, or even take remote control of a vehicle, posing serious threats to passengers and pedestrians alike. Moreover, with over-the-air updates and constant software integration, the attack surface of CAVs continues to expand, requiring a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity. Regulatory bodies, automakers, and tech companies must work collaboratively to establish stringent security protocols, conduct rigorous vulnerability testing, and foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness. By embedding security into every layer of the CAV ecosystem—from hardware and software to data management and user interaction—we can ensure that these technological marvels fulfill their potential without compromising safety and trust.
The Rise of CAVs and the Inherent Cybersecurity Risks
The rapid proliferation of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs) is being propelled by the seamless integration of transformative technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G connectivity, and advanced artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies collectively enable CAVs to gather, process, and respond to massive volumes of real-time data, creating a smart and dynamic mobility ecosystem. IoT sensors embedded in vehicles facilitate constant monitoring of vehicle performance, surroundings, and user behavior, while 5G networks ensure ultra-fast and low-latency communication for real-time decision-making. Meanwhile, AI algorithms empower CAVs with the ability to learn, adapt, and make autonomous choices in complex driving environments. This technological synergy underpins advanced driver-assistance features like adaptive cruise control, automatic emergency braking, and eventually, fully self-driving capabilities.
Central to the functionality of CAVs is their ability to communicate not only with one another (V2V) but also with infrastructure (V2I) such as traffic signals, road sensors, and smart city grids, as well as with cloud-based systems that host software updates, navigation data, and analytics platforms. This interconnected web of communication allows for smarter traffic flow, reduced fuel consumption, predictive maintenance, and improved road safety. For example, a CAV can receive real-time alerts about road hazards or congestion ahead and adjust its route or speed accordingly. Additionally, these vehicles can synchronize their movements with others nearby to minimize the risk of collisions and optimize travel efficiency. This vision of a connected transportation future brings with it the promise of more sustainable, safer, and user-centric mobility solutions.
However, the very interconnectedness that makes CAVs so innovative also introduces significant cybersecurity risks. Each point of communication—whether it’s a sensor, a cloud server, or a 5G signal—is a potential entry point for malicious attacks. Cybercriminals could exploit these vulnerabilities to intercept data, manipulate vehicle controls, or launch coordinated attacks across multiple vehicles and systems. For instance, unauthorized access to the vehicle’s network could allow hackers to disable safety features, track users’ movements, or even remotely hijack the vehicle. The complexity and scale of CAV networks mean that the attack surface is vast and constantly evolving. As a result, cybersecurity must be treated as a core pillar of CAV development, requiring continuous investment in secure software architecture, regular system updates, encryption protocols, and real-time threat detection mechanisms to ensure that the benefits of connected mobility are not overshadowed by preventable risks.
The risks associated with CAV cybersecurity are multifaceted and potentially catastrophic. Here are some key vulnerabilities:
- Unauthorized Access: Hackers could gain control of a vehicle’s systems, manipulating steering, braking, and acceleration. This could lead to accidents, injuries, and even fatalities.
- Data Breaches: CAVs collect and transmit vast amounts of data, including location information, personal preferences, and driving habits. A data breach could expose sensitive information, compromising user privacy.
- Communication Network Vulnerabilities: CAVs rely on wireless communication networks, which are susceptible to jamming, spoofing, and man-in-the-middle attacks. These attacks could disrupt communication between vehicles and infrastructure, leading to traffic chaos and safety hazards.
- Software and Firmware Vulnerabilities: Like any software-driven system, CAVs are vulnerable to bugs and exploits. Malicious actors could exploit these vulnerabilities to gain control of vehicle systems or inject malware.
- Physical Attacks on Hardware: Though less common, physical access to vehicle hardware can allow malicious actors to tamper with systems, install backdoors, or disable safety features.
The Importance of Cybersecurity in the CAV Ecosystem
The importance of cybersecurity in the connected and autonomous vehicle (CAV) ecosystem cannot be overstated. It is not merely a technical consideration to be addressed in the later stages of development, but a fundamental requirement that must be embedded from the very beginning. As CAVs become an integral part of modern transportation systems, ensuring their digital security is essential to protecting human lives, maintaining user privacy, and preserving the integrity of the entire mobility infrastructure. A single vulnerability in the system can have far-reaching consequences, from causing traffic disruptions to enabling large-scale cyberattacks with catastrophic outcomes.
Addressing cybersecurity in the CAV landscape requires a multi-layered and proactive approach. It involves securing hardware and software components, implementing robust encryption and authentication protocols, and continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities through real-time threat detection systems. Collaboration between automakers, tech companies, governments, and cybersecurity experts is also vital to establishing unified standards and sharing threat intelligence. Ultimately, treating cybersecurity as a foundational element—rather than an afterthought—will not only safeguard the technology itself but also help create a safer, smarter, and more resilient transportation future.
- Safety: The primary concern is safety. A cyberattack that compromises a vehicle’s control systems could have devastating consequences. Ensuring the integrity and reliability of vehicle systems is crucial for preventing accidents and protecting lives.
- Consumer Confidence: Public trust is essential for the widespread adoption of CAVs. Consumers need to be confident that their vehicles are secure and that their personal data is protected. A single high-profile cyberattack could erode public trust and hinder the growth of the CAV market.
- Financial Loss Prevention: Cyberattacks can lead to significant financial losses for both manufacturers and consumers. These losses can include the costs of recalls, repairs, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
- Regulatory Compliance: As CAVs become more prevalent, governments and regulatory bodies are developing cybersecurity standards and regulations. Compliance with these standards is essential for manufacturers to operate legally and maintain public trust.
Strategies for Enhancing CAV Cybersecurity
To mitigate the risks associated with CAV cybersecurity, a multi-layered approach is necessary. Here are some key strategies:
- Secure Software Development: Manufacturers must adopt secure software development practices, including rigorous testing, code reviews, and vulnerability assessments. Secure coding practices should be implemented at every stage of the development lifecycle.
- Encryption: Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive data transmitted between vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud-based services. Strong encryption algorithms should be used to protect data in transit and at rest.
- Authentication and Authorization: Robust authentication and authorization mechanisms are needed to prevent unauthorized access to vehicle systems. Multi-factor authentication, digital signatures, and access control lists can enhance security.
- Robust Communication Security: Securing communication networks is crucial for preventing attacks such as jamming, spoofing, and man-in-the-middle attacks. Secure communication protocols and intrusion detection systems should be implemented.
- AI for Threat Detection: Artificial intelligence and machine learning can be used to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time. Anomaly detection algorithms can identify suspicious activity and alert security personnel.
Cybersecurity Testing and Validation
Rigorous cybersecurity testing and validation are critical to ensuring the safety and reliability of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs). Techniques such as penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security audits help identify weaknesses in both software and hardware systems. These methods simulate potential cyberattacks and uncover flaws that could be exploited, allowing developers to address them proactively before vehicles hit the road.
Regular testing is not a one-time process but an ongoing necessity, especially as CAVs receive updates and interact with new systems. As the threat landscape evolves, continuous monitoring and reassessment are vital to maintain strong defenses. By embedding cybersecurity validation throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle, manufacturers can better protect passengers, data, and the broader transportation ecosystem.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Secure OTA update mechanisms are crucial for patching vulnerabilities and deploying security updates. Manufacturers must ensure that OTA updates are authenticated and encrypted to prevent tampering.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Implementing IDPS within the vehicle’s network and systems can help to detect and prevent malicious activities in real time.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Deploying SIEM systems allows for centralized monitoring and analysis of security logs and events, providing a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s security posture.
Challenges in Securing CAVs
Securing CAVs presents several unique challenges:
- Complexity of Vehicle Systems: CAVs are complex systems with numerous interconnected components. Securing these systems requires a holistic approach that addresses vulnerabilities at every level.
- Supply Chain Risks: CAVs rely on a complex supply chain involving numerous vendors and suppliers. Ensuring the security of the entire supply chain is essential for preventing the introduction of vulnerabilities.
- Emerging Threats: The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new cyber threats emerging regularly. Manufacturers must stay ahead of the curve and adapt their security measures accordingly.
- Legacy Systems: Many vehicles still in operation contain legacy systems that were not designed with modern cybersecurity standards in mind. Integrating these systems into the connected ecosystem poses a unique challenge.
- Standardization and Regulation: Establishing consistent cybersecurity standards and regulations across the automotive industry is crucial for ensuring interoperability and security. However, achieving consensus on these standards can be challenging.
- Resource Constraints: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures can be costly and resource-intensive. Manufacturers must balance security needs with cost considerations.
Conclusion: Driving Towards a Secure Future
The future of transportation is inextricably linked to the successful deployment of CAVs. However, this future hinges on our ability to address the cybersecurity challenges that these vehicles present. Robust cybersecurity is not an optional feature but a fundamental requirement for ensuring the safety, reliability, and trustworthiness of CAVs.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the threats facing CAVs. A proactive and collaborative approach is needed to stay ahead of these threats. Manufacturers, researchers, policymakers, and cybersecurity experts must work together to develop and implement effective security measures. Continued investment in research and development, along with the establishment of clear standards and regulations, will be crucial for building a secure and sustainable CAV ecosystem.
By prioritizing cybersecurity, we can unlock the full potential of CAVs and usher in a new era of safe, efficient, and connected mobility. The road ahead may be complex, but with diligence and foresight, we can ensure that the digital revolution in transportation is both transformative and secure.

The Future of Automotive Retail: Online Sales and Virtual Showrooms
The automotive retail industry is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the digital revolution reshaping consumer behavior. Traditional brick-and-mortar dealerships are no longer the sole avenue for car sales. Instead, online platforms and virtual showrooms are rapidly becoming integral to the car-buying experience. This blog explores how these digital innovations are revolutionizing the industry and what they mean for both consumers and dealerships.
Introduction
The internet has redefined the way consumers shop for everything—including cars. Buyers today demand a seamless, digital-first experience, from researching vehicle specifications to securing financing and scheduling test drives. This shift has forced automotive retailers to rethink their sales strategies, integrating cutting-edge technology to meet evolving consumer expectations. The rise of online sales platforms and immersive virtual showrooms marks a significant milestone in the automotive industry, bridging the gap between digital convenience and physical dealership engagement.
The Rise of Online Car Sales
Remember the days of spending countless weekends hopping from one brightly lit dealership to another? The pressure of negotiating prices, the endless brochures, the lingering feeling of uncertainty? Well, the automotive landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the same force that revolutionized retail, entertainment, and even grocery shopping: the internet. The rise of online car sales isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental change in how we buy one of the most significant purchases of our lives.
Click, Compare, Cruise: The Empowered Consumer
The convenience and accessibility of online platforms have irrevocably altered consumer purchasing habits, and car buying is no exception. Gone are the mandatory dealership visits just to get a feel for different models or compare prices. Today’s car buyer wields the power of information at their fingertips.
Online car sales platforms have become treasure troves of knowledge. Comprehensive vehicle specifications, unbiased expert reviews, and intuitive side-by-side comparison tools empower buyers to make informed decisions from the comfort of their homes. Forget the awkward dance of negotiation; transparent pricing models are becoming the norm, offering clarity and eliminating the traditional stress associated with securing a fair deal.
This digital shift is also ushering in an era of unparalleled personalization. Online configurators allow you to be the architect of your dream car, selecting preferred trims, colors, and a plethora of additional features. This tailored approach resonates deeply with modern buyers who expect convenience and complete control over their purchasing journey. And the ultimate cherry on top? Home delivery services are increasingly becoming a reality, allowing you to finalize your purchase and have your brand-new vehicle delivered directly to your doorstep – talk about convenience!
Beyond Brochures: Immersive Online Experiences with Virtual Showrooms
As online car sales gain momentum, the automotive industry is embracing cutting-edge technologies to bridge the gap between the digital and physical. Enter virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), transforming the online browsing experience into something truly immersive.
Virtual showrooms are no longer a futuristic fantasy; they’re a tangible reality. From the comfort of your couch in Bahadurgarh, you can virtually step inside a car, explore its every nook and cranny with 360-degree views, and zoom in on intricate details thanks to high-resolution visuals. Interactive demonstrations bring infotainment systems, safety features, and driving modes to life, offering an engaging way to understand a vehicle’s capabilities without ever setting foot in a physical showroom.
Augmented reality takes this a step further, allowing you to project a digital representation of your potential new car into your actual surroundings.
Imagine seeing how that sleek SUV looks parked in your driveway or visualizing its size next to your existing vehicle. This enhanced perspective provides a level of confidence and familiarity that traditional online browsing simply couldn’t offer.
The Best of Both Worlds: Embracing the Hybrid Future
Despite the undeniable surge of digital automotive retail, the physical dealership isn’t going anywhere just yet. While online platforms offer unparalleled convenience for research and initial selection, they can’t fully replicate the experience of a test drive, a hands-on inspection, or the personal interaction with a sales representative.
This is where the hybrid model shines. It’s about blending the best of both worlds – leveraging digital tools for the initial stages of the car-buying journey while preserving the valuable aspects of the traditional dealership experience. Customers can now embark on their journey online, researching models, customizing their preferences, and even securing financing before heading to a dealership to finalize their decision with a test drive and the necessary paperwork. The rise of “click-and-collect” services further exemplifies this trend, allowing buyers to complete most of the purchase online and visit the showroom solely for the final stages.
Post-purchase services are also integral to this hybrid approach. While online platforms streamline the buying process, after-sales support – including maintenance, servicing, and warranty assistance – remains a crucial function of physical dealerships. Many dealerships are now integrating digital tools for appointment scheduling, remote diagnostics, and service tracking, further enhancing customer convenience and loyalty.
Navigating the Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
The transition to digital sales, while brimming with advantages, also presents challenges that automotive retailers must navigate to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.
Meeting heightened consumer expectations is paramount. Accustomed to seamless online transactions in other industries, buyers expect the same level of efficiency and user-friendliness from automotive retailers. This necessitates significant investment in intuitive websites, sophisticated virtual showrooms, and streamlined financing options.
Building trust in high-value online transactions is another critical hurdle. Unlike smaller online purchases, buying a car involves a substantial financial commitment. Ensuring price transparency, providing comprehensive vehicle histories, and showcasing reliable customer reviews are essential in fostering confidence and security among online buyers.
Data security and privacy are also growing concerns. As dealerships collect sensitive customer data, robust cybersecurity measures and transparent privacy policies are non-negotiable to protect consumer interests.
However, these challenges are accompanied by significant opportunities. Expanding market reach is a major advantage of online sales. Traditional dealerships were often limited to their local customer base, but digital platforms unlock the potential for nationwide or even international sales.
Furthermore, customer engagement is being revolutionized through immersive and interactive experiences. Virtual showrooms, AI-powered chatbots offering real-time assistance, and personalized online interactions create a more engaging and tailored buying journey. Dealerships can also leverage the power of data analytics to optimize inventory management, predict demand trends, and tailor marketing efforts to specific customer segments, leading to greater efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The Evolving Dealership: From Transaction Hub to Experience Center
The rise of online car sales doesn’t spell the doom of the physical dealership; rather, it necessitates a fundamental evolution of its role. No longer solely a place for transactions, the dealership of the future is morphing into an experience center, a hub for building relationships and providing high-touch services that the digital realm can’t fully replicate.
One crucial aspect of this transformation is the emphasis on the sensory experience. While virtual showrooms offer impressive visuals, they can’t replicate the feel of premium leather, the scent of a new car interior, or the visceral thrill of hearing an engine roar to life. Dealerships are leveraging this by creating engaging physical spaces that go beyond rows of parked cars. Think comfortable lounges, interactive displays showcasing technology, and dedicated areas for personalized consultations. The focus shifts from a purely transactional environment to one where potential buyers can immerse themselves in the brand and the vehicle.
Test drives remain a cornerstone of the car-buying process, and this is where physical dealerships retain a significant advantage. The ability to get behind the wheel, feel the responsiveness of the steering, experience the ride quality, and assess the vehicle’s real-world performance is an indispensable part of the decision-making process. Dealerships are adapting by offering more flexible test drive options, including extended drives and even the possibility of taking a vehicle home overnight. This hands-on experience builds confidence and allows buyers to truly connect with the car before committing to a purchase.
Furthermore, dealerships are becoming centers for expert advice and personalized guidance. While online platforms provide a wealth of information, navigating the complexities of different models, financing options, and after-sales services can still be daunting. Knowledgeable sales representatives play a crucial role in understanding individual needs, answering specific questions, and providing tailored recommendations. This human element, the ability to build rapport and trust, remains a vital component of the car-buying journey, especially for such a significant investment.
The after-sales service department is also evolving into a key differentiator for dealerships. While online platforms can facilitate appointment scheduling and provide service updates, the physical act of servicing and maintaining a vehicle still requires a physical presence. Dealerships are investing in state-of-the-art service facilities, highly trained technicians, and streamlined processes to ensure a positive ownership experience. Building long-term relationships through reliable and efficient after-sales support fosters customer loyalty and encourages repeat business.
The Technological Arms Race: Innovation Driving Digital Automotive Retail
The digital automotive retail space is characterized by a constant influx of technological innovation, each new development aiming to enhance the online buying experience and bridge the gap between the digital and physical realms.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly significant role. AI-powered chatbots are becoming sophisticated enough to answer a wide range of customer queries, provide personalized recommendations based on browsing history and preferences, and even guide users through the financing process. Virtual assistants can schedule test drives, provide real-time inventory updates, and offer proactive support, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The evolution of virtual and augmented reality continues to push the boundaries of online car shopping. We’re seeing more realistic and interactive virtual showrooms that allow for detailed customization and even virtual test drives using VR headsets. AR applications are becoming more refined, enabling potential buyers to visualize vehicles in their own driveways with greater accuracy and even explore interior features in detail through their smartphones or tablets.
Blockchain technology holds the potential to revolutionize transparency and trust in the automotive industry. By providing a secure and immutable record of a vehicle’s history, including ownership, maintenance, and accident reports, blockchain can address concerns about used car fraud and build greater confidence in online transactions.
Data analytics is becoming an indispensable tool for automotive retailers. By analyzing vast amounts of customer data, dealerships can gain valuable insights into buyer behavior, predict demand trends, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize pricing strategies. This data-driven approach allows for more targeted and effective customer engagement, ultimately leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
The integration of online and offline systems is also crucial. Seamless data flow between a dealership’s website, CRM system, and physical inventory allows for real-time updates and a consistent customer experience across all touchpoints. This omnichannel approach ensures that customers can start their journey online and seamlessly transition to an in-person experience without losing any information or encountering inconsistencies.
The Road Ahead is Digital, But Not Entirely Virtual
The future of automotive retail is undeniably digital. Online sales platforms and virtual showrooms are reshaping the industry, offering unprecedented convenience, transparency, and personalization. While the role of the traditional dealership is evolving, it’s far from obsolete.
The hybrid model, seamlessly blending online research and transactions with the tangible experiences offered by physical dealerships, ensures that customers receive the best of both worlds. As technology continues its relentless march forward, the automotive retail landscape will continue to transform, creating a more seamless, engaging, and efficient car-buying experience for everyone.
The digital revolution isn’t replacing dealerships; it’s transforming them for the better, paving the way for a future where buying your dream car is as enjoyable and convenient as browsing your favorite online store. So buckle up, the automotive journey has just entered a thrilling new digital era.
